Roof climate research

When designing a roof garden plan for your client you put a lot of time and effort into making sure that each plant is fit for its spot. Ideally, plants that prefer shade and moist soil should not be planted in full sun. But sometimes this thought-out plan seems to not correspond to reality. Giving us an unpleasant surprise.
Constructing the base for a planted roof can be done throughout most of the year, but actually putting plants into the substrate should be kept for the end of autumn throughout early spring. This gives you some good opportunities to monitor the natural conditions that occur on your client's roof!
In this blog we will discuss how you can conduct the right kind of roof climate research for your client's roof garden
Avoid lanky succulents
Not all parts of a roof receive the same amount of sunlight, which is why roof climate research is so important. Sometimes other buildings in the area can cast rather large areas of shade upon the roof. It would be a waste of time and resources to plant the most sun-loving succulents on this part of the green roof. More shade-loving plants like Viola odorata would do much better here.
As a roof garden constructor, you often have to ask your clients about sunlight on the roof. Unfortunately, many clients don't have a good idea about this or are overly confident about the amount of sunlight a particular spot receives. Blindly planting sedum mats in this spot turns into a lanky disaster.
Special PAR lamps or sunlight provide the right spectrum for a plant to grow healthy and strong. To make sure that you plant the right vegetation in the right spot, it would be wise to do some more in-depth studies about what parts of the roof receive what amount of sunlight by monitoring your garden roof.
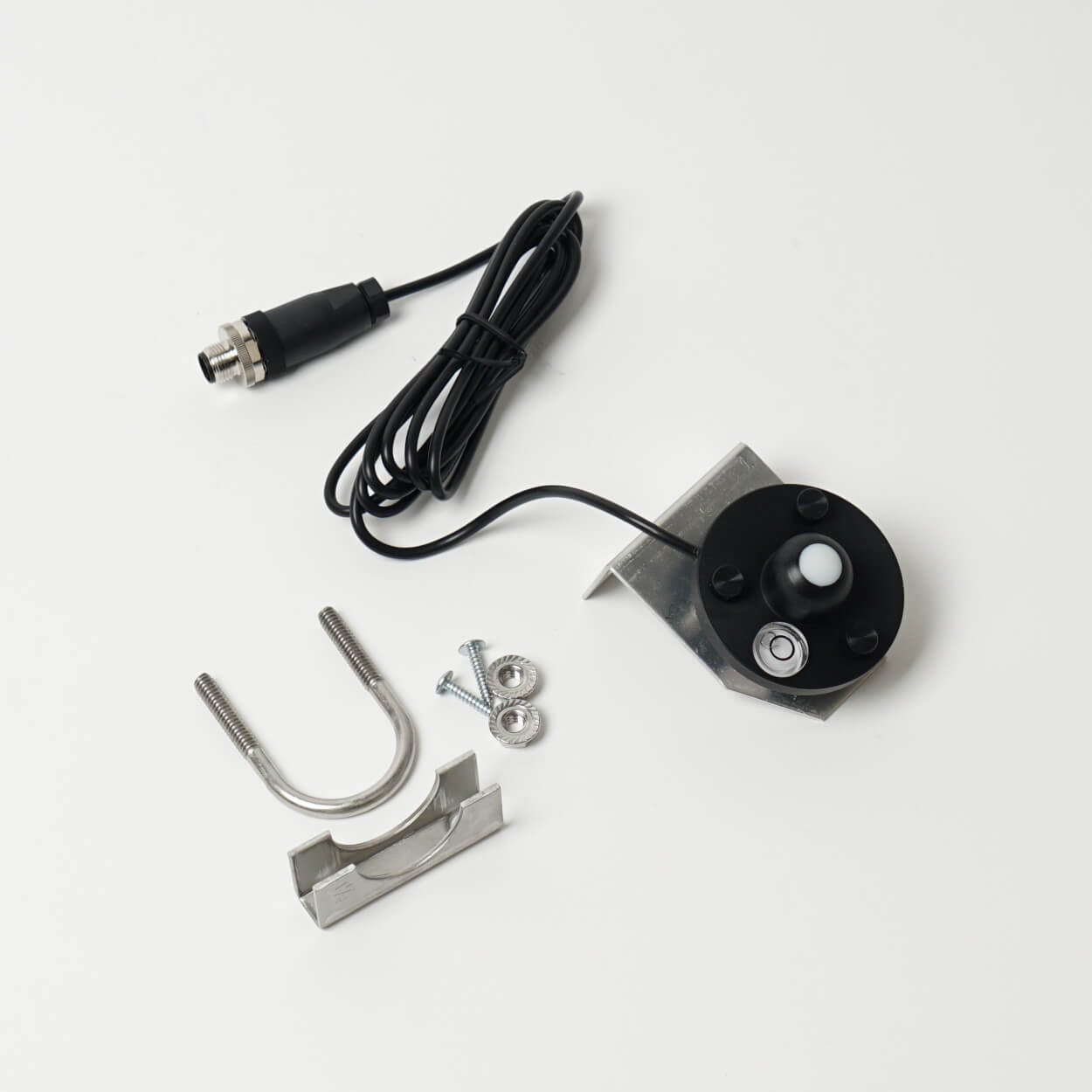
To carry out these studies a PAR sensor should be installed into the barren substrate. Make sure to place the sensor in all the different zones, collecting data for at least a week per zone. At the end of your research, you can add these measurements to your plan, giving you the right information to determine which plant goes where.

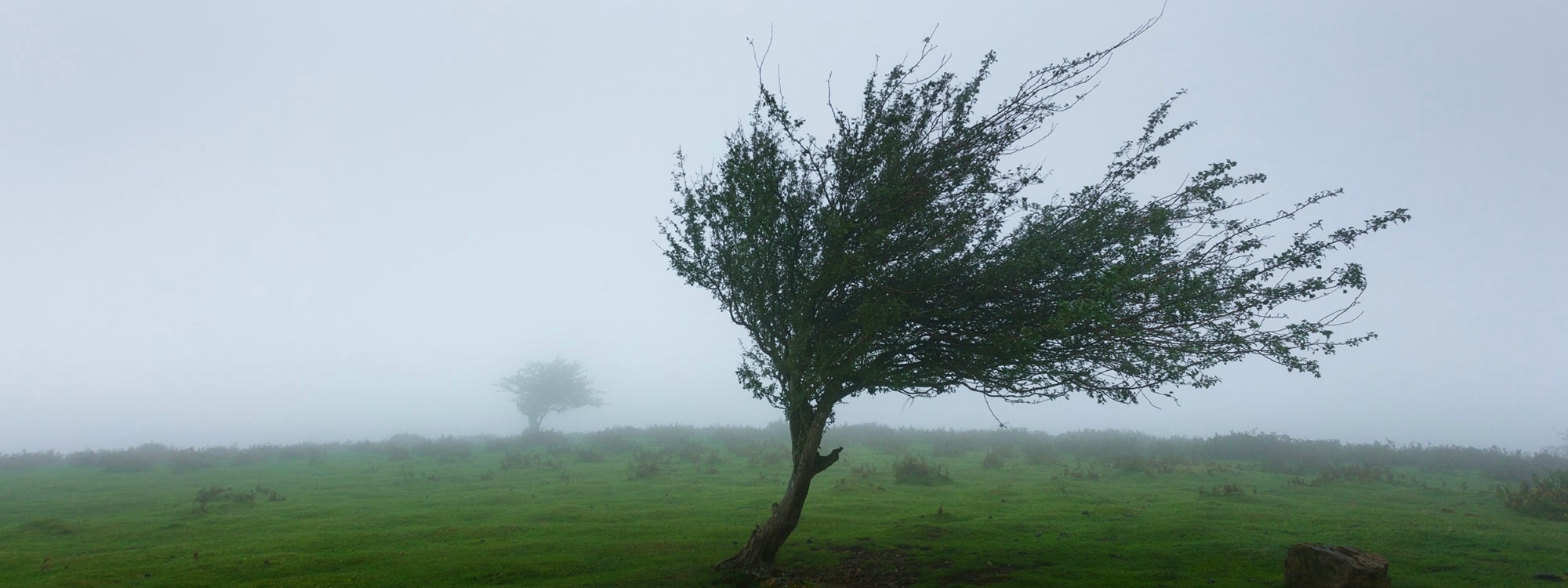
Do not get blown away by surprises
A garden roof (or intensive green roof) is typically known for its small trees and shrubbery. Especially on large buildings at large heights, we need to account for wind. We cannot just plant a tree on a 30-story building without putting any thought into it. How much wind does this spot get? How often? How strong are the winds? Or perhaps: what spot is the best choice - windwise - to plant the tree?
A windmeter or wind sensor would happily provide you with this data as it measures windspeed and wind direction. When installed during the windiest part of the year it can give you a pretty accurate idea of the challenges your roof-tree is going to face. This also gives you more insights into how strong the anchoring holding the tree in place should be.
If you choose to install a weather station to measure and monitor wind, you can measure the following interesting parameters at the same time: rain, temperature and relative humidity.

No drowned Sedum or shrivelled Echinacea
A typical extensive green roof is known for its vast array of tiny sedums, but semi-extensive roof gardens often feature more herbaceous plants such as Gaura, Echinacea and Verbena. They all fare well with a little more moisture in the substrate while sedums are tough as nails.
Unpleasant surprises such as the outlets of rain gutters onto the roof tend to mess with our plans. At the same time, we sometimes overlook a wall or higher roof preventing rain from reaching the garden roof.
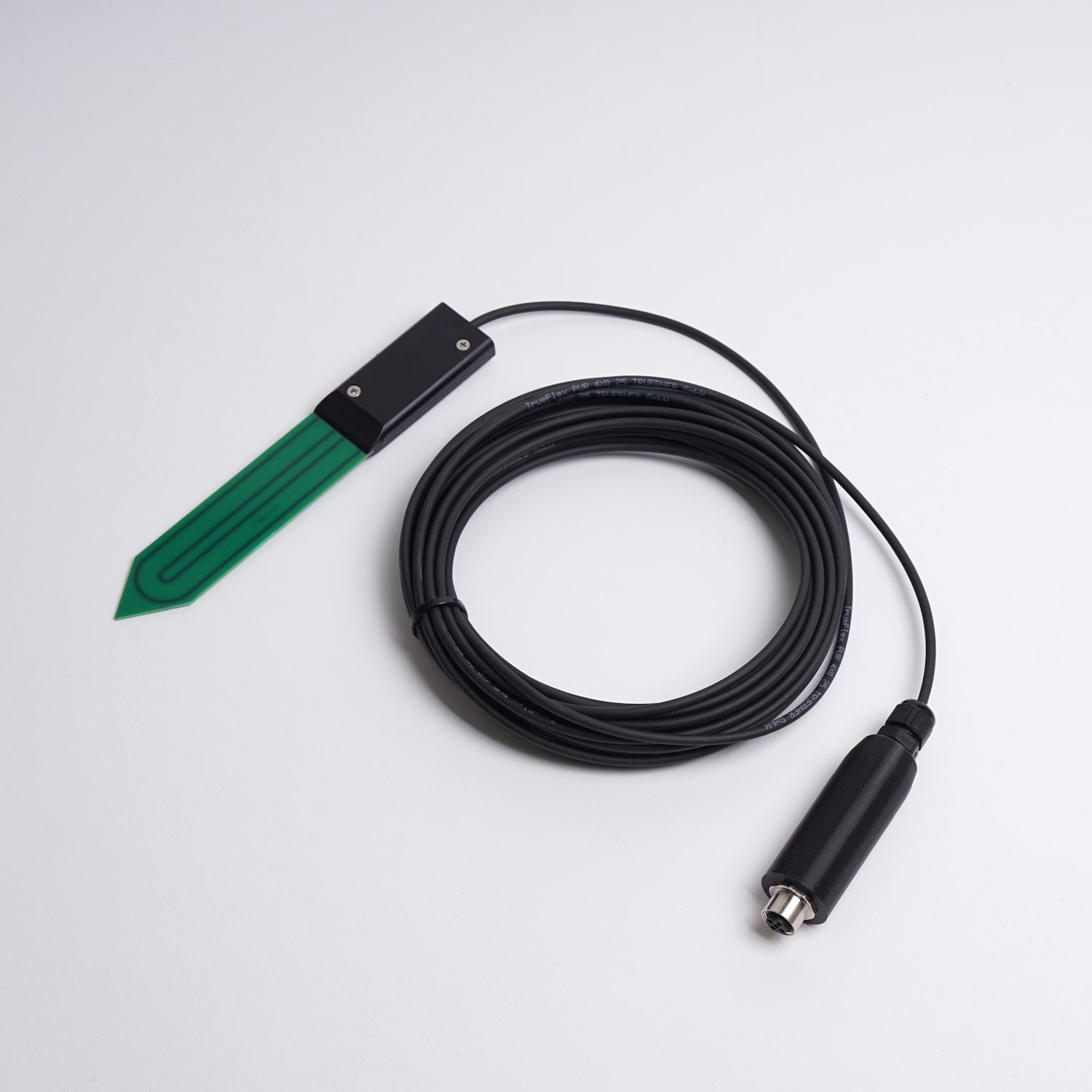
To make sure that your herbaceous plants receive the right amount of moisture, it would be advised to take some soil moisture measurements in the zones you wanted to plant them. The same goes for drier zones that were intended for succulents, as these plants should never be in swampy soil. We all know that the healthier the plants are, the less likely they are to succumb to pests and diseases.
Measuring and monitoring the soil moisture in your plain substrate before planting vegetation gives you the opportunity to choose the best plants for the right zone. A soil moisture sensor collects data about the naturally occurring moisture levels in your green roof. Over a longer period of time, these data will even give you a better insight into how quickly soil moisture decreases relative to temperature. Optimising vegetation also means limiting irrigation later on, making the green roof even more green and more sustainable in water use!

Why use Reporter?
Of course you could buy several individual sensor systems to measure soil moisture levels, PAR levels or register wind on your roof garden. But do these tools also gather their data in one central place or do they even let you view historical data at all?
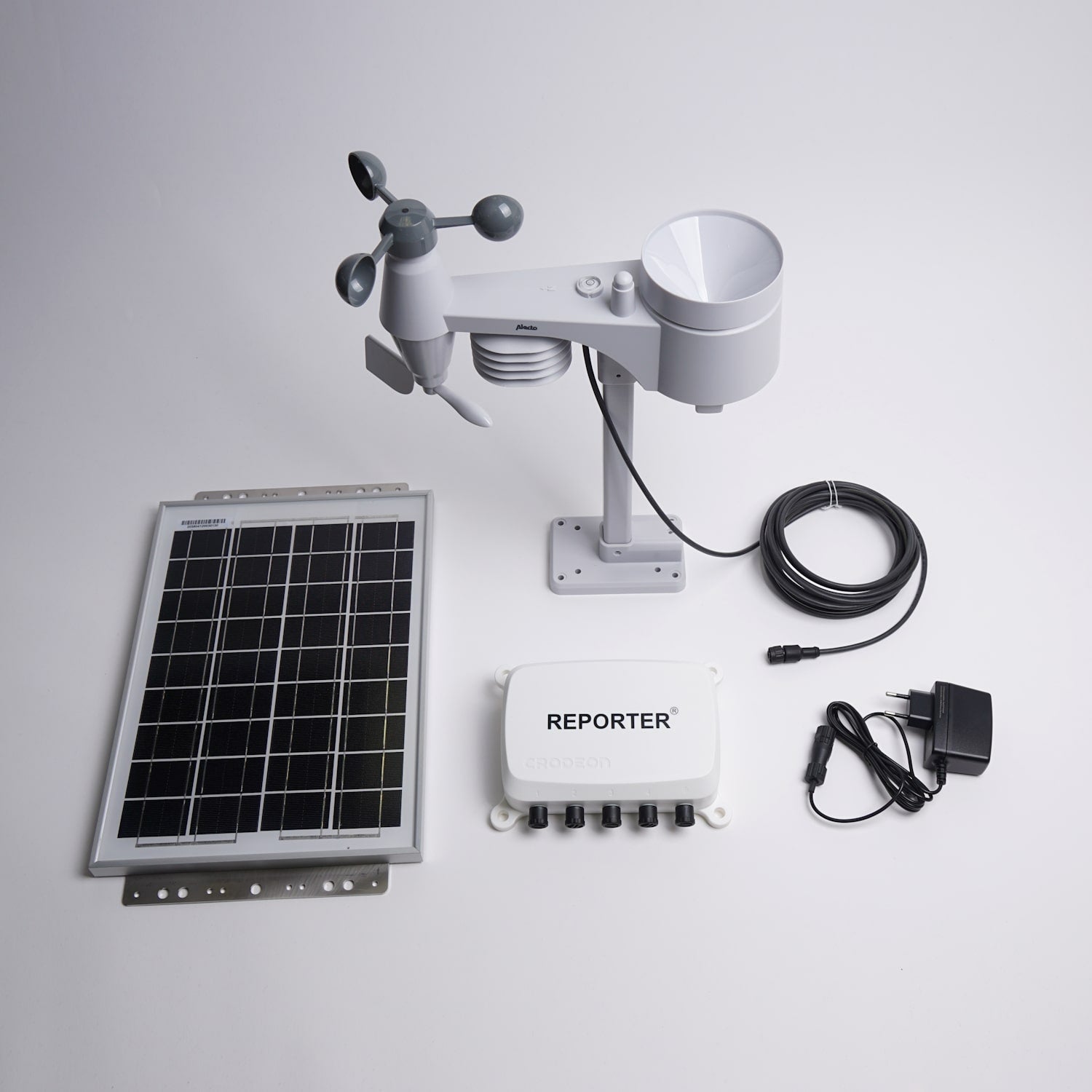
Reporter is the tool that will help you help your client. It lets you connect up to 4 sensors onto one module. For instance: one weather sensor, two soil moisture sensors, and one PAR sensor. The remote monitoring system Reporter sends its measurements to the cloud (Crodeon Dashboard) in real-time, which means that you can do an online follow-up on the green roof 24/7. The system is waterproof, mobile and autonomous, meaning that its internet connection works through its integrated SIM card. Power can be supplied to Reporter and the weather station with a solar panel (grid power works too). Even the most remote roofs that have no power outlets or poor wifi connections can be measured and monitored by Reporter.
Sensors are compatible in whatever combination you desire and they work plug & play. You could thus take your PAR sensor and weather station with you after your research, to use them again at your next big project.
Last but not least: Reporter lets you set alarm thresholds. When a threshold is about to be reached Reporter will send an alarm notification to your phone. Giving you the opportunity to respond ASAP!
Start your roof climate research
Stop wasting time and money replanting vegetation that failed to grow, when you can conduct some basic research beforehand. Reporter helps you conduct your roof climate research to optimise your green roof project.
Don't hesitate to contact us if you have any questions.
Read more about green roofs: