What is the difference between ultrasonic and electromagnetic flow meters?
When you want to measure the flow rate of a liquid you start looking for a flow meter. But diving deeper into the world of flow meters quickly starts getting more complicated. Several kinds of flow meters exist and they aren't all interchangeable. What is the difference between ultrasonic and electromagnetic flow meters? We'll be discussing the differences below.
What is an electromagnetic flow meter?
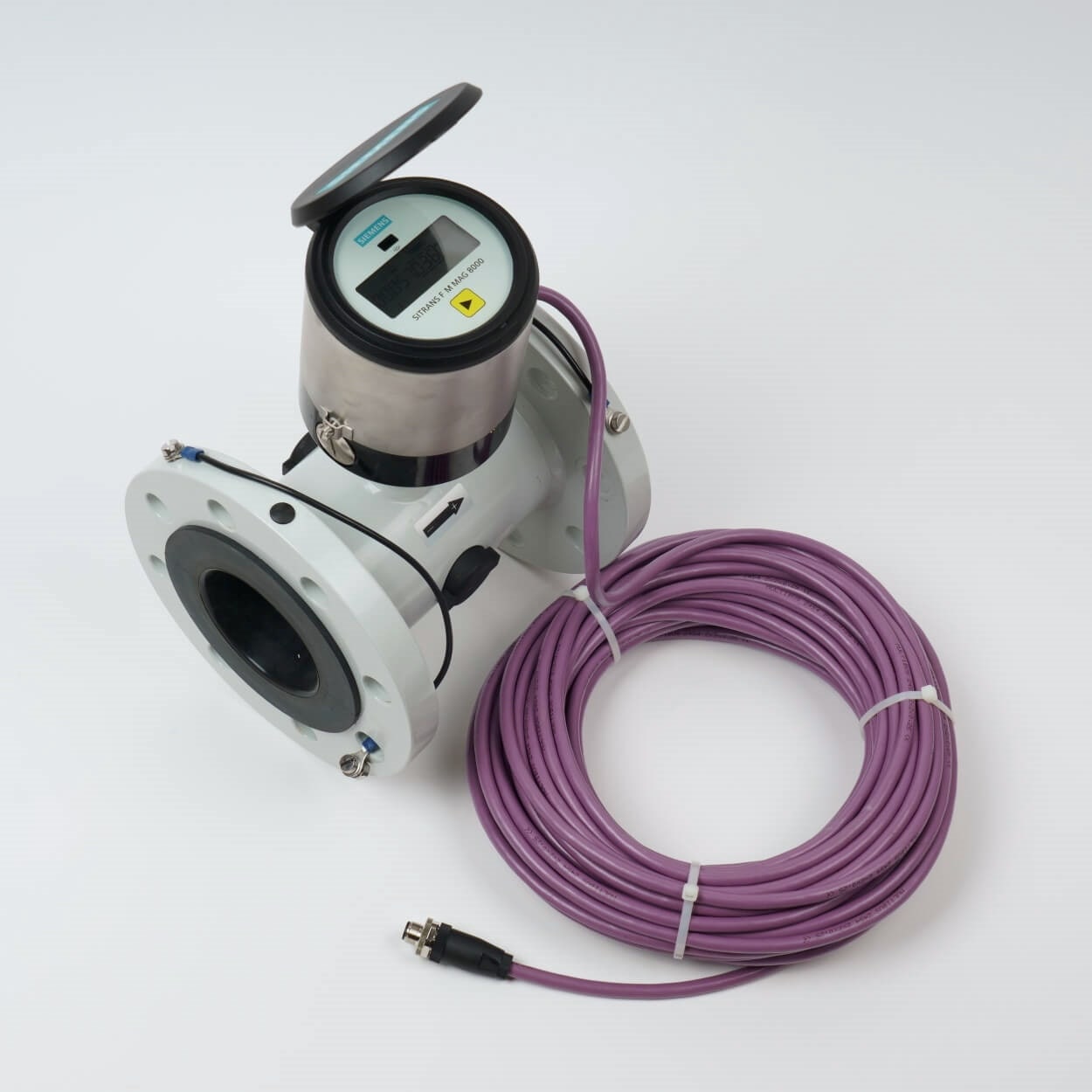
Electromagnetic flow meters only work when the substance they measure is conductive (liquids, like water). They work according to Faraday's law of induction. The flow meter creates a magnetic field, and the liquid that passes through the meter contains positive and negative ions. The magnetic field will separate these + and - ions, causing a voltage difference to appear in the liquid. The quicker the liquid flows, the more electricity (voltage) will be generated.
Electromagnetic flow meters are usually applied to installations that are meant for measuring water or waterbased (chemical) liquids.
What works: drinking water, rainwater, groundwater, waterbased solutions, acids, alkaline solutions and more.
What doesn't work: distilled water (because it is not conductive), fossil oils (hydrocarbons), and gases.

The biggest difference between electromagnetic and ultrasonic flow meters probably lies in that electromagnetic flow meters work solely on conductive liquids, whereas ultrasonic flow meters do not have this restriction.
Electromagnetic flow meters have some big advantages however, they do not obstruct the flow that they're measuring. This means that even liquids with a high viscosity can be measured. Even sludge, mud or liquid manure, which can contain solid pieces. Additionally, these flow meters are able to withstand high temperatures and high pressure.
What is an ultrasonic flow meter?
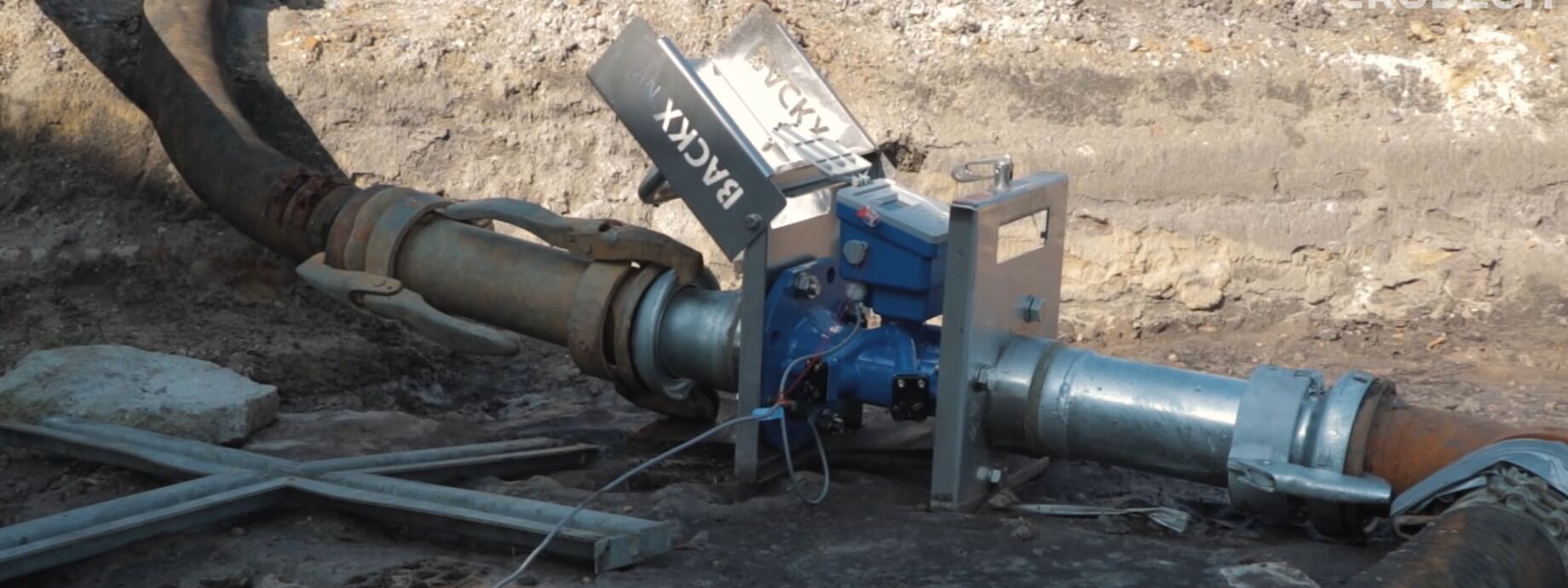
An ultrasonic flow meter is another kind of non-obstructing flow meter that can measure liquids with a limited viscosity. The way in which flow is measured however differs from the electromagnetic flow meter. Ultrasonic flow meters work by sending out ultrasonic (sound) pulses. The meter contains at least 2 sound transmitter-receivers. The speed of the measured medium is determined by the difference of the transit time at which the pulse travels between the transmitters and the receivers.
What works: clean fluids (no solids), gases and fossil oils (hydrocarbons).
What doesn't work: ultrasonic flow meters are sensitive to solids (more than 5 to 10%) or bubbles.

The biggest difference between ultrasonic and electromagnetic flow meters is that ultrasonic flow meters do not require a conductive liquid to work. They also measure gases but fare less well with liquids that contain many solids or bubbles. Ultrasonic meters are able to withstand high temperatures and high pressure. Along with being able to withstand aggressive fluids (in case of clamp-on ultrasonic flowmeters).
What is the difference between electromagnetic and ultrasonic flow meters?
The biggest differencebetween ultrasonic and electromagnetic flow meters is how they measure (and consequently what they can measure). Electromagnetism works based on whether a liquid is conductive and flow is measured based on electricity. Ultrasonics work based on sound pulses and measure the time between emitting and receiving a pulse. Ultrasonic flow meters can measure gases, liquids and vapours, while electromagnetic flow meters work solely on (conductive) liquids.
Last but not least, it's worth noting that electromagnetic flow meters are often cheaper than ultrasonic flow meters.
|
Can measure
|
Electromagnetic flow meters
|
Ultrasonic flow meters
|
| Non-conductive liquids | no | yes |
| Liquids containing more than 10% solids or bubbles | yes | no |
| High pressure | yes | yes |
| High or low temperatures | yes | yes |
| These media | liquids | gases, liquids, vapours |
The best choice for your project
There are some minor differences between electromagnetic and ultrasonic flow meters. Depending on your specific situation you will have to choose what flow meter works best for you.
Learn more about our Smart Water solutions.